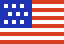
Average temperature profile for the lower layers of the atmosphere

Average temperature profile for the lower layers of the atmosphere

The envelope of gas surrounding the Earth changes from the ground up. Five distinct layers have been identified using
- thermal characteristics (temperature changes),
- chemical composition,
- movement, and
- density.
Each of the layers are bounded by "pauses" where the greatest changes in thermal characteristics, chemical composition, movement, and density occur.

Exosphere
This is the outermost layer of the atmosphere. It extends from about 375 miles (600 km) to 6,200 miles (10,000 km) above the earth. In this layer, atoms and molecules escape into space and satellites orbit the earth. At the bottom of the exosphere is a transition layer called the thermopause.
Thermosphere
Between about 53 miles (85 km) and 375 miles (600 km) lies the thermosphere, known as the upper atmosphere. While still extremely thin, the gases of the thermosphere become increasingly denser as one descends toward the Earth.
As such, incoming high energy ultraviolet and x-ray radiation from the sun begins to be absorbed by the molecules in this layer and causes a large temperature increase.
Because of this absorption, the temperature increases with height. From as low as -184°F (-120°C) at the bottom of this layer, temperatures can reach as high as 3,600°F (2,000°C) near the top.
However, despite the high temperature, this layer of the atmosphere would still feel very cold to our skin. The high temperature indicates the amount of the energy absorbed by the molecules, but with so few molecules in this layer, the total number would not be enough to heat our skin.
Take it to the MAX! The Ionosphere: The Outer Edges of the Atmosphere
The bottom of the thermosphere is the mesopause - the transition into the mesosphere.
Mesosphere
This layer extends from around 31 miles (50 km) above the Earth's surface to 53 miles (85 km). The gases that comprise this layer continue to become denser as one descends. As such, temperatures increase as one descends, rising to about 5°F (-15°C) near the bottom of this layer.
The gases in the mesosphere are now thick enough to slow down meteors hurtling into the atmosphere, where they burn up, leaving fiery trails in the night sky. Both the stratosphere (next layer down) and the mesosphere are considered the middle atmosphere. The transition boundary which separates the mesosphere from the stratosphere is called the stratopause.
Stratosphere
The stratosphere extends from 4 -12 miles (6-20 km) above the Earth's surface to around 31 miles (50 km). This layer holds 19 percent of the atmosphere's gases but very little water vapor.
In this region, the temperature increases with height. Heat is produced in the process of the formation of ozone, and this heat is responsible for temperature increases, from an average -60°F (-51°C) at tropopause to a maximum of about 5°F (-15°C) at the top of the stratosphere.
This increase in temperature with height means warmer air is located above cooler air. This prevents convection as there is no upward vertical movement of the gases. As such, the location of the bottom of this layer is readily seen by the anvil-shaped tops of cumulonimbus clouds
The transition layer at the bottom of the stratosphere is called the tropopause.
Troposphere
Known as the lower atmosphere, almost all weather occurs in this region. The troposphere begins at the Earth's surface, but the height of the troposphere varies. It is 11-12 miles (18-20 km) high at the equator, 5½ miles (9 km) at 50°N and 50°S, and just under four miles (6 km) high at the poles.
As the density of the gases in this layer decrease with height, the air becomes thinner. Therefore, the temperature in the troposphere also decreases with height. As one climbs higher, the temperature drops from an average around 62°F (17°C) to -60°F (-51°C) at the tropopause.
Average temperature profile for the lower layers of the atmosphere