When you think of springtime on land, you might think of birds migrating, flowers blooming, and leaves emerging. While these changes are happening on land, changes are happening in the ocean, too!
But how can you tell if spring has sprung in the sea? This graphic explains some of the seasonal effects that take place as ocean waters warm and days grow longer.
We’re sharing this during springtime in the Northern Hemisphere, but these effects also take place when it's spring in the Southern Hemisphere. See our changing seasons resource collection to learn more.
Upwelling
As weather patterns change in the spring, surface waters in some regions are pushed offshore by wind and replaced by cold, nutrient-rich water that “wells up” from below. In these regions, the nutrient-rich water encourages the growth of marine life, leading to high productivity during the springtime.
Phytoplankton bloom
Phytoplankton, which are tiny microscopic plants, grow quickly and in large quantities as more sunlight is available and surface waters get warmer. The annual spring bloom is an ecologically important occurrence that fuels many ocean ecosystems and can even be seen by satellites in space.
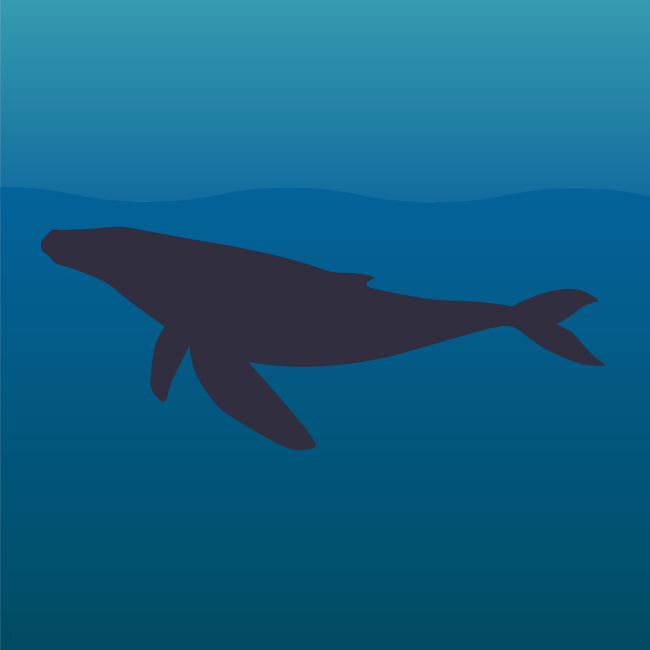

Whale migration
Humpback whales travel great distances during their seasonal migration between cold, productive summer feeding habitats and warm, shallow winter mating and calving waters. During springtime, they migrate back to colder waters, bringing their new calves with them.
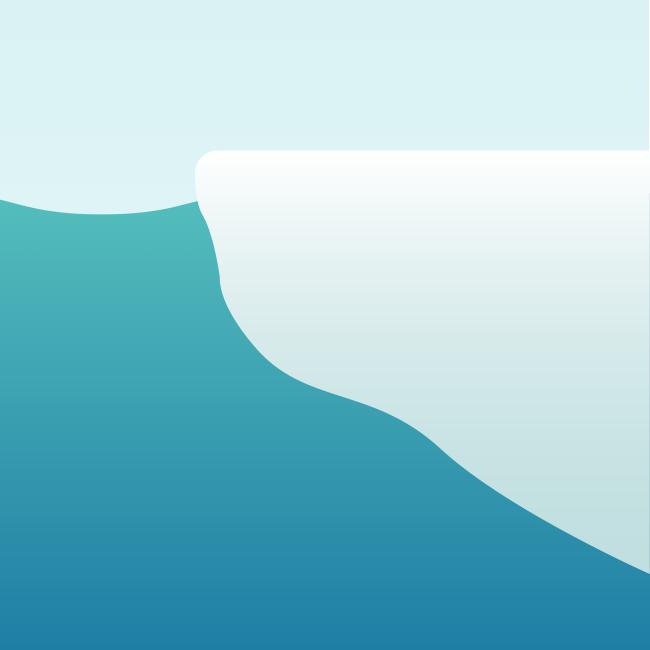

Sea ice extent
Sea ice forms, grows, and melts in the ocean as sunlight availability and temperatures change throughout the seasons. The annual maximum extent, when there is the most sea ice, occurs in early spring. Sea ice decreases through spring and summer to come to an annual minimum extent in early fall.

